

-
[Natural Factors]
- Lightning Strikes
- Mountain Fire
- Snowstorms
- Line Faults
- Overgrown Vegetation
- Flash Over
- Animals
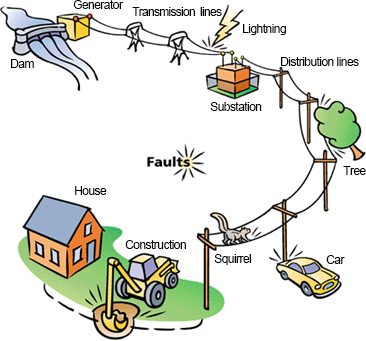
[Artificial Factors]
Failure of Power Supply System Equipment
-In case of failure due to a lightning strike, etc. on the transmission line, instantaneous voltage drop occurs when the faulty equipment is disconnected by opening the breaker.
-When a ground fault or short circuit accident occurs in the power system, an instantaneous voltage drop and an instantaneous power failure occur while the accident point is disconnected.
Start of Large Capacity Load
- Instantaneous voltage drop occurs due to peak current when starting a large capacity load
-
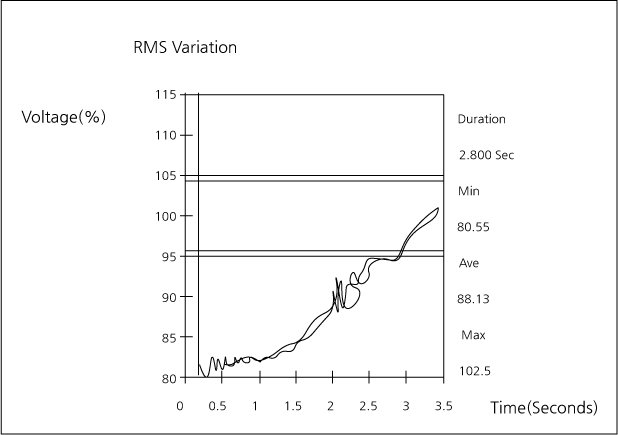
Instantaneous voltage drop rate (%) within 150km from the lightning strike place
-
Sag caused by Lightning Strike
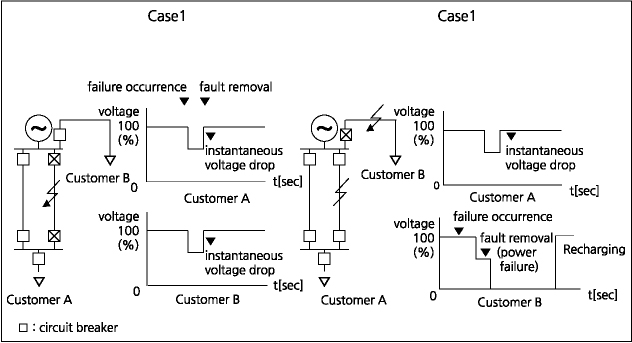
When a failure occurs due to lightning strike, etc. on the transmission line constituting the power system, it is necessary to detect and disconnect the highway fault facility from the system to minimize damage to the facility or to minimize the fluctuation of voltage and to maintain the stability of the power system.
Detect the failure point with the protective relay installed in each facility of the transmission line, etc. and if it is determined that the facility under protection has failed, open the breaker to remove the failure facility. An instantaneous voltage drop occurs while the fault is removed.
-
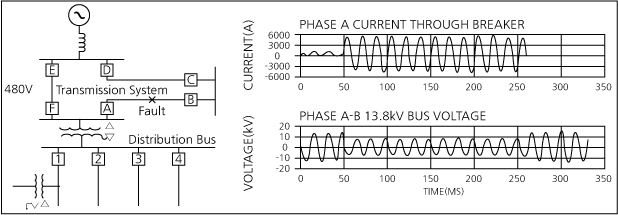
Sag occurrence due to Ground Fault or Short Circuit
When 1-line ground fault, 2-line ground fault and a short circuit, or 3-phase short circuit accident occur in the power system, the accident point is disconnected and voltage sag and interruption occur while the fault is removed. As shown in the figure below, when an accident occurs on the transmission line, the A·B circuit breaker operates to generate a voltage sag while the accident point is disconnected.
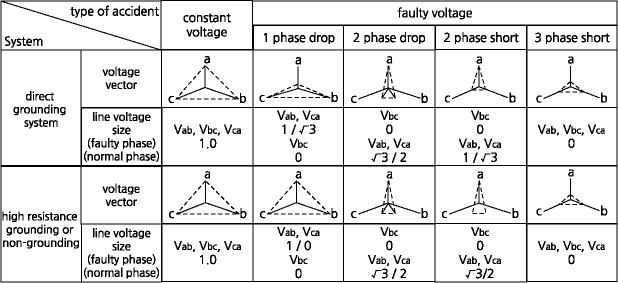
The voltage drops by accident type of the system vary depending on the neutral point grounding method. The degree of voltage drop for 1-line ground fault is small in a non-grounded and high-resistance grounding system, and gets large in a direct grounding system. The degree of voltage drop for two-phase and three-phase ground faults is large regardless of the system grounding method.
[The difference in voltage drop due to the system accident in terms of voltage vector is as follows.]
-
Sag Occurrence due to Large Capacity Load
As the power facility gets larger, the capacity of the motor gets larger, resulting in a voltage sag due to the starting current generated during startup.
-
Occurrence Path of instantaneous voltage drop due to operation of (Re-Closing Circuit) of KEPCO transmission facility arising from lightning strike
